CRANK, NO-START: THE MOST COMMON CAUSES
Does your car crank but fails to start? There could be many potential causes for this issue. In this article, we’ll try to break it down in the easiest way possible. So hopefully, after reading this, you’ll be able to diagnose what’s causing a crank no start condition.
Let’s start with the basics. For the engine to start, it needs the correct amount of air(14.7), the correct amount of fuel (1), and a spark. In addition, it needs the correct timing. To be more specific, mechanical timing and electrical timing. When it comes to mechanical timing, the timing chain needs to synchronize the camshafts and the crankshaft. This helps the valves and the pistons to move at the correct time during the 4-stroke cycle. When it comes to electrical timing, there needs to be fuel and spark commanded at the correct time. In coil-on-plug and waste spark systems, this is controlled by the engine control module (ECM) through an algorithm. It uses sensors to help achieve this. With all this in mind, anything disrupting air, fuel, spark, or timing could cause a crank no-start.
scan for trouble codes
The first and easiest way to help you determine what is causing a crank no-start is to scan your vehicle for trouble codes. This will give you a good starting point to figure out what’s wrong with your vehicle. If your car is made after 1996, you can use an OBD2 scanner.
fuel system
When it comes to the fuel system, you want to start by measuring the pressure on the fuel rail. You can measure it by using a fuel pressure gauge, or in some vehicles, you can use an OBD2 scanner, if the car has a fuel rail pressure sensor. You want to make sure the fuel pressure is within spec according to your repair manual. In some situations, you might not have access to measure the fuel pressure. In this case, you can remove a nut and see if fuel comes out. If everything looks good, you could conclude that the fuel system is not part of the problem. On the other hand, if you have low fuel pressure it could be caused by a weak fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter.
Another instance could be no pressure at all. Here is a list starting from the least challenging to the most challenging components to identify and diagnose:
Empty tank
Fuel pump fuse
Fuel pump relay
Fuel pump
Extremely clogged fuel filter
Fuel pump control module
It’s important to note that the ECM can disable fuel if it notices a crucial problem with the engine. So, make sure to read the codes and fix those problems before concluding the fuel system is at fault.
Air system
A quick tip is to press down on the gas pedal and crank the engine at the same time. If your car turns on, then you could have one of the three problems that we’re about to discuss.
The first issue with the air system could be a clogged idle air control valve. Its purpose is to allow air to enter the engine when the car is stationary. If gets extremely clogged or is stuck-closed, it can restrict the airflow, which disrupts the air-fuel ratio required for the engine to start.
The next potential cause is a dirty throttle plate. If the throttle plate gets extremely dirty, it can get stuck closed. When this happens, it will prevent the right amount of air from coming into the engine. This disrupts the air-fuel mixture and causes a no-start. You can clean the throttle body with a carburetor cleaner and a toothbrush. I’ll leave the cleaner in the description below.
The third potential cause could be a large vacuum leak. Now, the impact of a vacuum leak depends on its size. With a small vacuum leak, you may still be able to start the car, but it will likely result in a rough idle. However, if the vacuum leak is more significant, it’s possible that the vehicle won’t turn on. This is not as common though.
ignition system
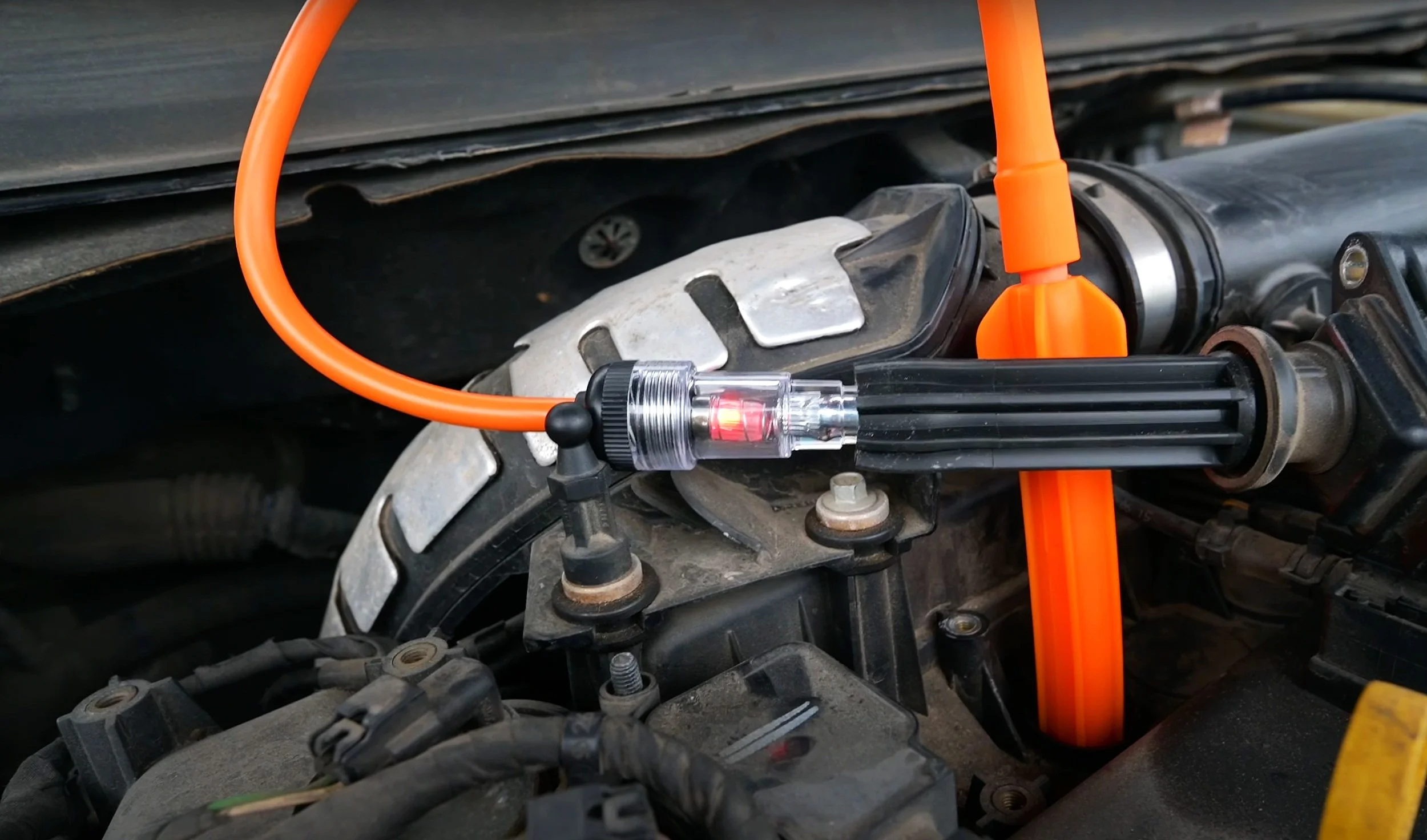
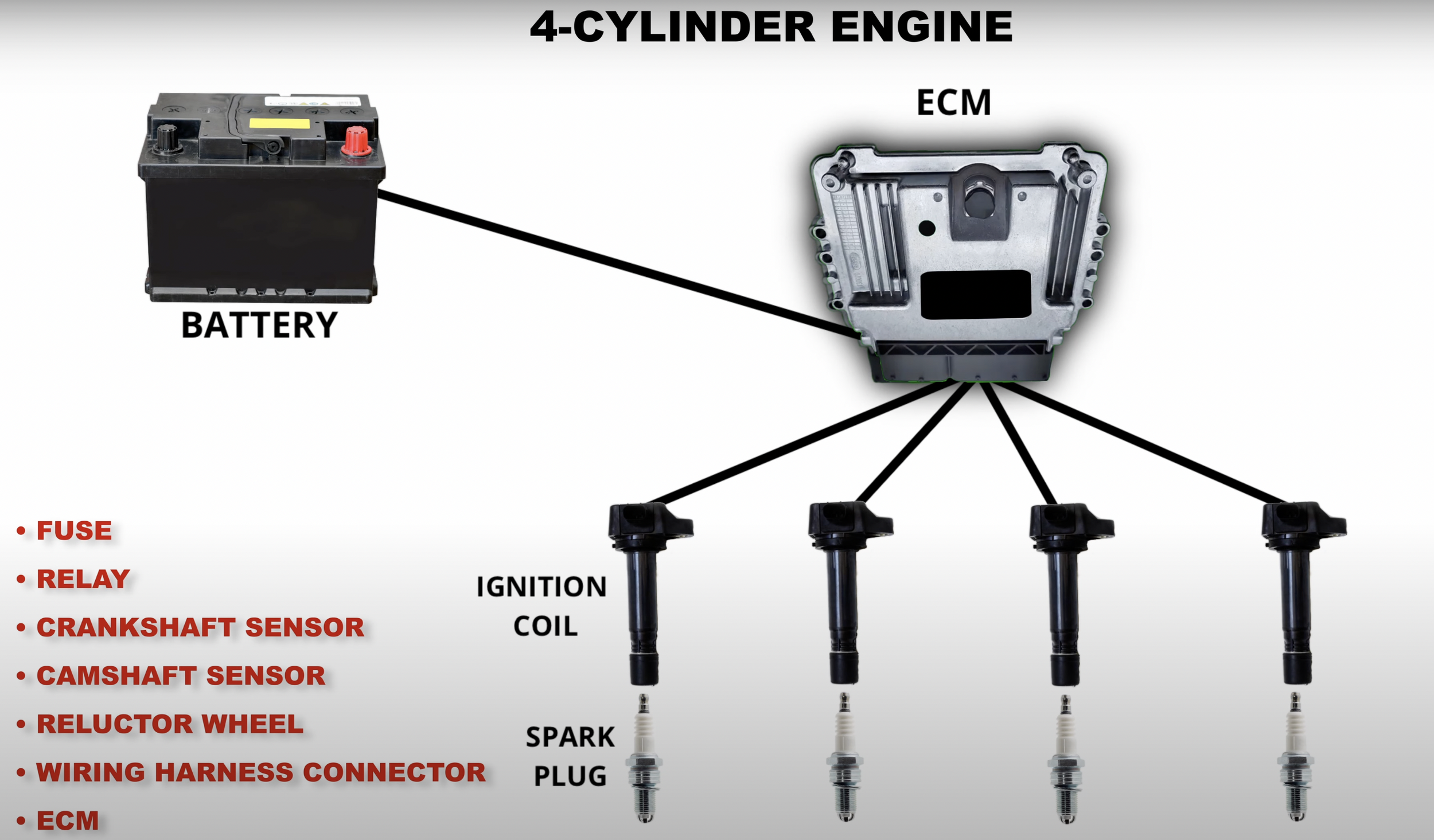
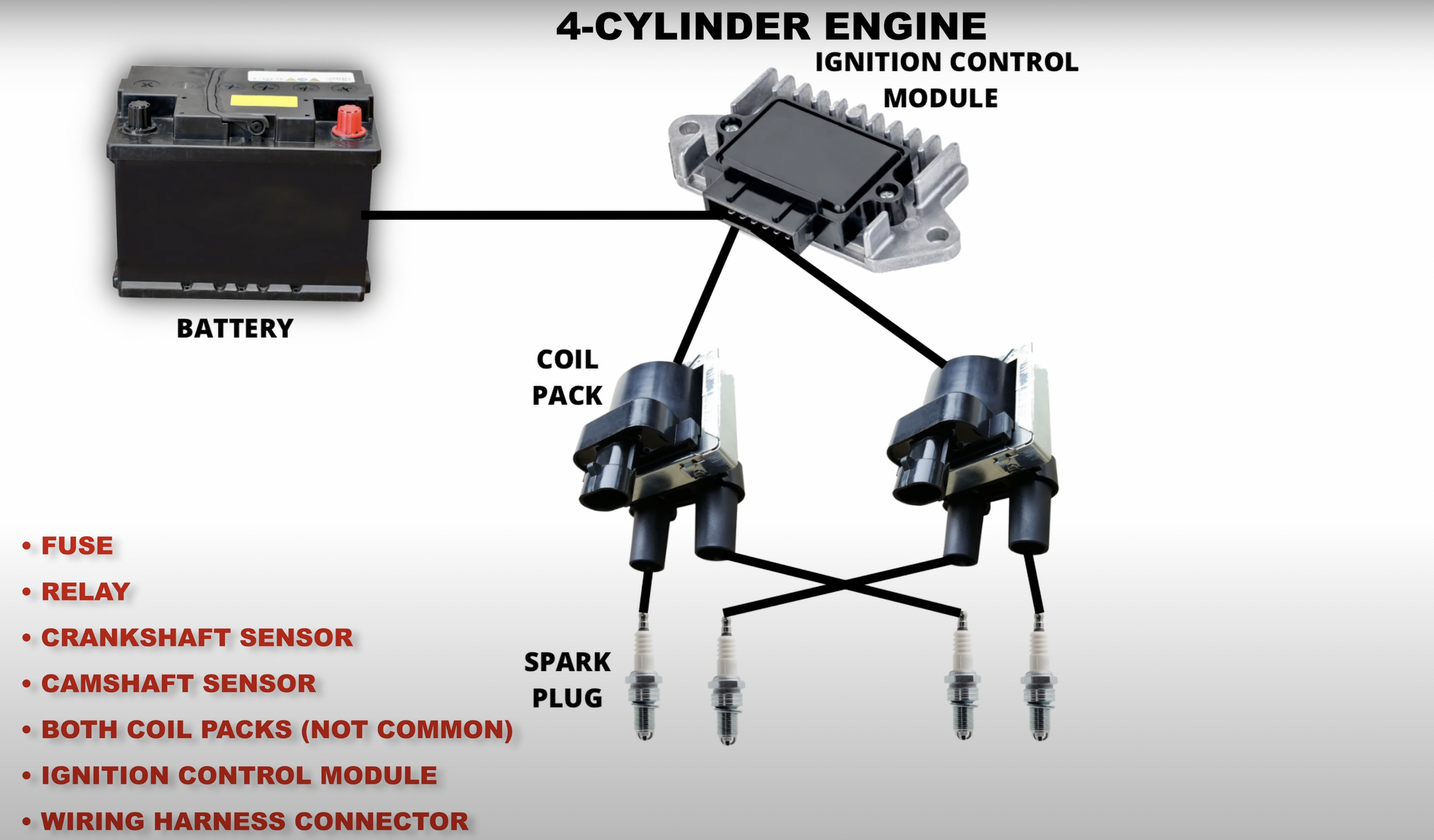
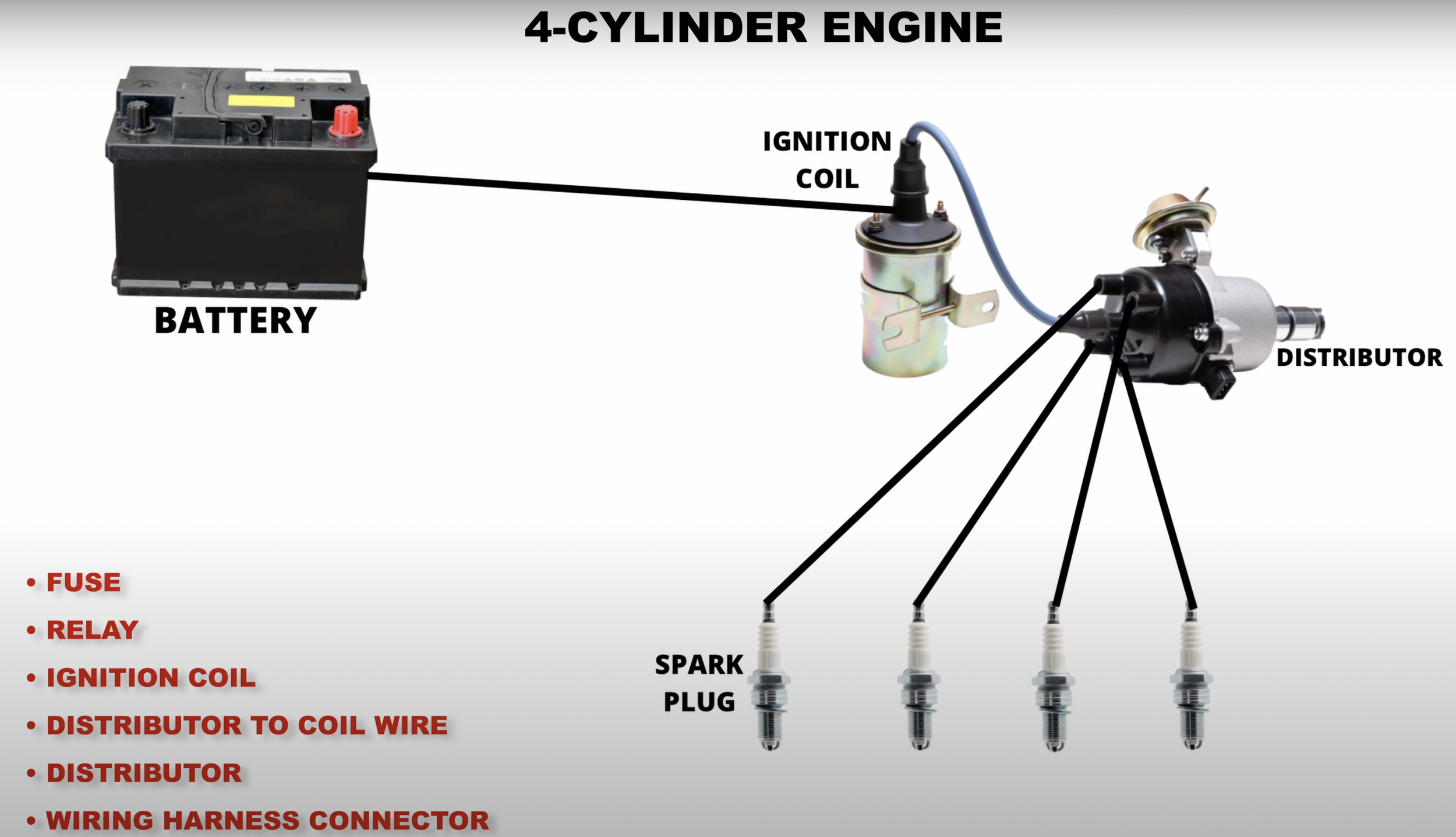
The first step of diagnosing the ignition system is by performing a spark test with the spark checker kit.
A blinking red light indicates that the spark plug produces a spark.
If you get a spark in all of your cylinders, then you can rule out the ignition system as the cause for the no-start. If you don’t get a spark in all the cylinders, you could have bad spark plugs or ignition coils. However, that’s very rare since the chances of all spark plugs or ignition coils going out at the same time are very low.
The next step is to figure out what type of ignition system your car has. For example, the coil-on-plug system, which is most commonly used today, a waste-spark system, or a distributor system. Let’s dive into every system and some potential causes (written in red).
Coil-On-Plug System
Waste-Spark System
Distributor System
If you have a COP or waste spark system, it’s important to consider that a faulty crankshaft position sensor could cause the ECM to purposely not command spark to protect your engine. So make sure to fix sensor problems before making your conclusion.
timing
Let’s move on to the next potential cause - timing. As stated before, there’s mechanical timing and electrical timing.
When it comes to mechanical timing, I'm referring to the timing chain or timing belt. If it breaks, the camshafts won't rotate, and as a result, the valves won't open. The only component that will continue rotating is the crankshaft, which typically leads to faster cranking resulting in a no start.
As for electrical timing I mean ignition timing. This is the timing for the spark to occur during the 4-stroke cycle. Now you may ask, how does the engine know when to command a spark? Well, this depends on the type of ignition system you have. Most waste spark and coil-on-plug systems use crankshaft and camshaft sensors to help achieve this. If you have a distributor it uses a magnetic sensor that’s housed inside, typically called a pickup coil. If any of these sensors malfunction then the spark timing could be off leading to a no-start. In some situations, the ECM purposely cuts power to the ignition coils until the problem is fixed.
compression
The next possible cause for a crank no start is an extreme loss of compression. This could be caused by a warped cylinder head, a blown head gasket, or a broken timing chain.
To determine if there is a lack of compression, you can perform a compression test using a compression tester.
sensors
Another important aspect to consider is engine sensors. Here’s a list of sensors utilized by the ECM to determine when to command a spark and add the correct amount of fuel for the combustion process:
Crankshaft sensor
Camshaft sensor
MAF Sensor
MAP sensor
Oil pressure sensor (some vehicles)
Throttle Position Sensor
If any of these sensors are malfunctioning, the ECM can prevent the vehicle from starting. Also, make sure to look for any torn wires or corrosion on the connectors of these sensors as this can create a similar result.
antitheft system
The next potential cause is a malfunctioning antitheft system. One common feature is an immobilizer system that requires a specific electronic code from the key or key fob to start the engine. If there's a problem with the immobilizer system, it won't recognize the correct code and won't allow the engine to start. If you see the anti-theft light on while turning the key, this could be the reason why you have a crank no-start.
exhaust system
The next cause is not very common but I have seen it happen. It’s a clogged exhaust system. To be more specific, a clogged catalytic converter. An extremely clogged catalytic converter can cause a crank no-start situation because it restricts the engine's ability to release exhaust gases. Similar to how we breathe, the engine needs to draw in fresh air and release exhaust gases. If it can't effectively release the exhaust gases, it won't be able to take in new air for the combustion process. This disrupts the air-fuel mixture and causes a no-start.
ecm/bcm
The last potential cause is computer system issues. Even though this is not as common, it’s still something to consider. If any of the computers like the ECM or BCM are malfunctioning in your vehicle, they can either send out wrong information or lose communication completely leaving you with a crank no-start.
If you are a DIY enthusiast, I recommend getting a repair manual here. You can use code “AD10VA” for 15% off one-year subscriptions for any US Order.
Check out my YouTube video!
Disclaimer: Some links in this article may be affiliate links.